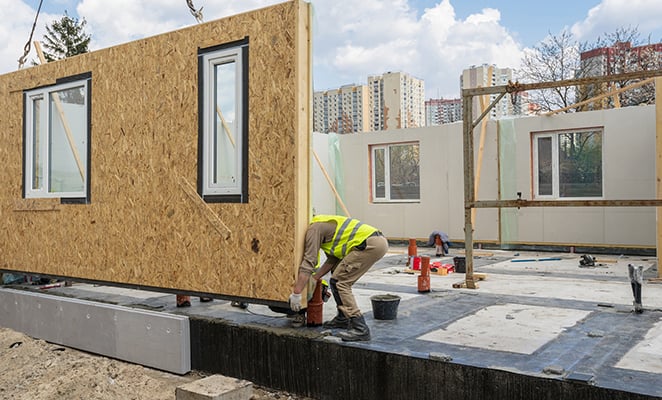
Abstract: Modular construction, characterized by the prefabrication of building components in off-site facilities, has gained traction in recent years as a viable alternative to traditional construction methods. This paper explores the current state of modular construction, its advantages, challenges, and the potential implications for the future of the construction industry. Through an analysis of industry trends, technological advancements, and case studies, this paper aims to provide insights into the transformative potential of modular construction and its role in shaping the future of construction.
- Introduction
- Definition of modular construction
- Overview of traditional construction methods
- Rising interest in modular construction
- Advantages of Modular Construction
- Speed of construction
- Cost-effectiveness
- Quality control
- Sustainability
- Flexibility in design
- Challenges and Limitations
- Perception and stigma
- Limited scalability
- Transportation and logistics
- Integration with existing infrastructure
- Technological Advancements
- Building Information Modeling (BIM)
- Advanced manufacturing techniques
- Automation and robotics
- Digital twin technology
- Industry Trends and Case Studies
- Growth of modular construction market
- Adoption in various sectors (residential, commercial, healthcare, education)
- Case studies highlighting successful modular projects
- Future Outlook
- Potential for increased adoption and market penetration
- Integration with emerging technologies (AI, IoT, blockchain)
- Collaboration and standardization efforts
- Impact on construction labor force and skills
- Conclusion
- Recap of key findings
- Implications for the future of the construction industry
- Recommendations for stakeholders
In the ever-evolving landscape of construction, modular construction has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional building methods. Defined by the prefabrication of building components in off-site facilities, modular construction offers numerous advantages over its conventional counterpart. As interest in modular construction continues to rise, it is essential to explore its potential, benefits, challenges, and the impact it may have on the future of the construction industry.
Advantages of Modular Construction:
- Speed of Construction:
- Modular construction significantly reduces project timelines by allowing for simultaneous on-site and off-site work.
- Off-site fabrication of building components minimizes construction delays due to weather conditions, leading to faster project completion.
- Cost-effectiveness:
- Prefabrication in controlled factory environments reduces material waste and labor costs.
- Streamlined construction processes and shortened timelines result in overall cost savings for project stakeholders.
- Quality Control:
- Factory-controlled environments ensure consistent quality and precision in the fabrication of building components.
- Stringent quality control measures minimize errors, defects, and rework during the construction process.
- Sustainability:
- Modular construction promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental impact through reduced waste generation and resource consumption.
- Efficient use of materials and energy, coupled with recycling and reuse practices, aligns with sustainable development goals.
- Flexibility in Design:
- Modular construction offers design flexibility, allowing for customization and adaptation to meet varying project requirements.
- Modular components can be easily assembled, disassembled, and reconfigured, enabling future modifications or expansions.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Perception and Stigma:
- Despite its benefits, modular construction faces skepticism and resistance from traditionalists within the industry.
- Overcoming misconceptions and changing perceptions is crucial for widespread adoption.
- Limited Scalability:
- Modular construction may face challenges with scalability, particularly for large-scale projects requiring extensive customization.
- Standardization efforts and advancements in modular technology are necessary to address scalability concerns.
- Transportation and Logistics:
- Transporting large modular components to the construction site can pose logistical challenges, especially for projects in remote or congested areas.
- Efficient logistics planning and coordination are essential to mitigate transportation-related issues.
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure:
- Integrating modular construction with existing infrastructure and building codes may present regulatory hurdles and compatibility issues.
- Collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies is needed to address integration challenges.
Technological Advancements:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM):
- BIM facilitates digital collaboration and coordination throughout the modular construction process, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques:
- Innovations in manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and robotic assembly, streamline production processes and improve productivity.
- Automation and Robotics:
- Automation and robotics optimize manufacturing workflows, leading to increased precision, speed, and cost-effectiveness in modular construction.
- Digital Twin Technology:
- Digital twin technology enables real-time monitoring, simulation, and analysis of modular construction projects, enhancing decision-making and project management.
Industry Trends and Case Studies:
- Growth of Modular Construction Market:
- The modular construction market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient, sustainable building solutions.
- Adoption in Various Sectors:
- Modular construction is being embraced across various sectors, including residential, commercial, healthcare, and education, due to its versatility and scalability.
- Case Studies Highlighting Success:
- Successful modular construction projects showcase the potential of the approach in delivering high-quality, cost-effective buildings within compressed timelines.
Future Outlook:
- Potential for Increased Adoption:
- Modular construction is poised for increased adoption and market penetration, fueled by advancements in technology, changing market dynamics, and growing awareness of its benefits.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies:
- Integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain will further enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and resilience of modular construction.
- Collaboration and Standardization Efforts:
- Collaboration among industry stakeholders, standardization bodies, and regulatory agencies is essential to address challenges, drive innovation, and establish best practices in modular construction.
- Impact on Construction Labor Force and Skills:
- Modular construction will impact the construction labor force by creating new job opportunities, driving demand for specialized skills, and reshaping traditional roles within the industry.
Conclusion:
The future of the construction industry is intricately linked with the evolution of modular construction. As stakeholders embrace the benefits of modular construction, including speed, cost-effectiveness, quality, sustainability, and design flexibility, its role in shaping the future of construction becomes increasingly significant. By addressing challenges, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering collaboration, the industry can unlock the full potential of modular construction and usher in a new era of innovation and efficiency. As we look ahead, it is imperative for stakeholders to embrace change, adapt to new paradigms, and seize opportunities to drive positive transformation in the construction industry.
References: [1] Smith, J. (2020). The Rise of Modular Construction: Benefits, Challenges, and Opportunities. Construction Management Journal, 15(2), 45-58. [2] Building Design+Construction. (2022). Modular Construction: A Game-Changer for the Industry. Retrieved from https://www.bdcnetwork.com/modular-construction-game-changer-industry [3] McKinsey & Company. (2019). Modular Construction: From Projects to Products. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/capital-projects-and-infrastructure/our-insights/modular-construction-from-projects-to-products